In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, companies are consistently looking for ways to boost efficiency, cut costs, and enhance operational performance. Lean manufacturing emerges as a strategic methodology focused on maximizing value while minimizing waste. By adopting lean principles, organizations can refine their processes, increase productivity, and achieve greater success in their respective markets.
What is Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing centers on eliminating waste and optimizing processes to deliver maximum value. This approach originated from Toyota’s Production System (TPS) and emphasizes the importance of streamlining production flow, ensuring that every step adds value to the end product. The objective is to provide high-quality goods while utilizing minimal resources, ultimately leading to reduced costs and improved efficiency.

How Lean Manufacturing Enhances Efficiency
The main aim of lean manufacturing is to identify and eliminate waste—any process that doesn’t contribute value. Waste can manifest in various ways, such as:
Overproduction: Creating more products than necessary.
Waiting: Idle time while waiting for materials or information.
Transportation: Unnecessary movement of goods.
Excess Motion: Unproductive movements by workers.
Overprocessing: Performing more work than needed.
Defects: Producing flawed products.
Unused Employee Skills: Not fully leveraging employee capabilities.
By addressing these forms of waste, lean manufacturing significantly improves operational efficiency.
Key Practices for Improvement
1. Streamlined Processes: Lean encourages ongoing evaluation and enhancement of workflows to remove bottlenecks, thus increasing throughput and reducing lead times.
2. Quality Enhancement: Emphasizing root cause analysis and standardized practices reduces defects and boosts customer satisfaction, leading to fewer resources spent on rework.
3. Flexibility: Practices like Just-In-Time (JIT) production allow companies to swiftly respond to market demands, optimizing resource usage.
4. Employee Engagement: Fostering a culture of continuous improvement empowers employees to contribute their insights, facilitating innovation and problem-solving.
Cost Reduction Through Lean Practices
Lean manufacturing effectively lowers costs in several ways:
Inventory Management: JIT strategies reduce inventory levels and related carrying costs, freeing up capital for other uses.
Lower Overhead: Streamlining processes minimizes unnecessary expenses, enhancing resource utilization.
Reduced Rework: Improved quality control and standardized processes lower the costs linked to defective products.

Implementing Lean Manufacturing
Successfully integrating lean manufacturing requires a strategic approach:
1. Evaluate Existing Processes: Identify inefficiencies and waste using tools like value stream mapping to visualize operations.
2. Engage the Workforce: Involve employees in the lean transformation to create a culture of continuous improvement.
3. Develop a Lean Strategy: Outline goals, strategies, and metrics to guide implementation.
4. Provide Training: Equip staff with the necessary skills to apply lean principles effectively.
5. Monitor Progress: Regularly assess performance metrics to evaluate the impact of lean initiatives and make adjustments.
6. Celebrate Achievements: Acknowledge milestones to reinforce the value of lean practices and motivate ongoing commitment.
In the fast-paced and competitive realm of manufacturing, businesses are continuously seeking innovative ways to optimize their operations. With rising costs and increasing consumer expectations, companies are under pressure to enhance efficiency, streamline processes, and cut unnecessary expenditures. Lean manufacturing stands out as a highly effective methodology designed to maximize value by eliminating waste throughout the production cycle. By integrating lean principles into their operations, organizations can achieve significant improvements in productivity, quality, and overall performance.
Understanding Lean Manufacturing
At its core, lean manufacturing is centered around the philosophy of delivering high-quality products while using the fewest resources possible. This approach has its roots in the Toyota Production System (TPS), which revolutionized manufacturing in the mid-20th century. Lean manufacturing emphasizes the importance of creating processes that not only focus on efficiency but also prioritize value creation for the customer. This means scrutinizing every aspect of production to ensure that each step contributes positively to the final product, ultimately reducing costs and enhancing customer satisfaction.
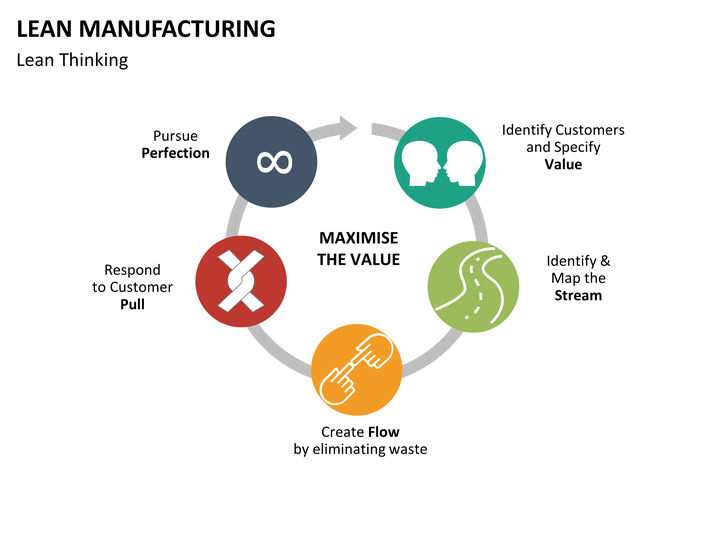
The Role of Waste Elimination
A fundamental aspect of lean manufacturing is the identification and elimination of waste, which encompasses any activity or process that does not add value from the customer's perspective. Lean practitioners classify waste into several categories, each representing different inefficiencies that can hinder operational effectiveness.
Overproduction: This occurs when production exceeds demand, leading to surplus inventory that incurs storage costs and potential obsolescence.
Waiting: Any idle time experienced by workers or machines while waiting for materials, instructions, or other resources is a form of waste that can disrupt workflow.
Transportation: Unnecessary movement of products or materials between locations not only wastes time but also increases the risk of damage and loss.
Excess Motion: Unproductive movements by employees, such as reaching for tools or walking long distances, can slow down processes and reduce efficiency.
Overprocessing: This involves doing more work or adding unnecessary features to a product that do not enhance its value for the customer.
Defects: Producing items that fail to meet quality standards results in rework or scrap, leading to wasted materials and labor.
Unused Employee Skills: Not leveraging the full potential and expertise of employees can limit innovation and efficiency.
By systematically addressing these forms of waste, lean manufacturing helps organizations enhance efficiency and drive significant cost savings.
Strategies for Enhancing Efficiency
The implementation of lean manufacturing involves several key strategies that contribute to operational improvement:
Streamlined Processes: Lean encourages a culture of continuous improvement, where processes are regularly reviewed and optimized. This proactive approach helps eliminate bottlenecks and redundancies, allowing for smoother workflows and increased throughput.
Quality Improvement: By focusing on quality at every stage of production, lean manufacturing reduces the likelihood of defects. Techniques such as root cause analysis enable companies to identify issues early in the production process, ensuring that the end product meets customer expectations.
Flexibility and Responsiveness: Lean practices such as Just-In-Time (JIT) production empower companies to respond quickly to fluctuations in market demand. This agility allows organizations to allocate resources more efficiently and adapt production schedules as needed.
Employee Engagement: A critical component of lean manufacturing is fostering a culture that encourages employee involvement. By engaging workers in problem-solving and decision-making processes, companies can tap into their collective knowledge, leading to innovative solutions and a more motivated workforce.

Achieving Cost Reduction
Implementing lean manufacturing can lead to substantial cost savings through various mechanisms:
Lower Inventory Costs: The application of JIT principles allows organizations to maintain minimal inventory levels, thereby reducing carrying costs and freeing up capital for other operational needs.
Reduced Overhead Expenses: Streamlined processes inherently lead to lower production costs by eliminating non-value-added activities. This reduction in overhead enhances overall resource utilization.
Minimized Rework and Waste: With an emphasis on quality and standardized work procedures, lean manufacturing reduces the occurrence of defects. This focus minimizes the costs associated with reprocessing defective products and decreases waste generation.
Steps to Successfully Implement Lean Manufacturing
The journey to adopting lean manufacturing principles requires a comprehensive and structured approach:
Evaluate Existing Processes: Begin by conducting a thorough assessment of current operations. Use tools like value stream mapping to visualize the flow of materials and information, identifying areas of inefficiency and waste.
Engage and Empower Employees: Involve team members at all levels in the lean transformation process. Encourage them to share their insights and participate actively in identifying problems and proposing solutions. A culture of continuous improvement thrives on employee engagement.
Develop a Comprehensive Lean Strategy: Outline a clear plan that details the goals, strategies, and specific actions needed to implement lean practices. This plan should include measurable objectives and timelines to track progress.
Provide Targeted Training: Equip employees with the knowledge and skills necessary to implement lean principles effectively. Training should encompass lean tools, techniques, and best practices to ensure a well-informed workforce.
Monitor and Assess Performance: Establish metrics to continuously evaluate the effectiveness of lean initiatives. Regularly analyze data to identify further improvement opportunities and make necessary adjustments.
Celebrate Milestones and Achievements: Recognize and celebrate successes throughout the lean transformation journey. Acknowledging accomplishments reinforces the importance of lean principles and motivates employees to remain committed to continuous improvement.

Core Lean Principles Beyond Waste Elimination
While waste elimination is the cornerstone of lean manufacturing, the methodology encompasses several other critical principles that contribute to its effectiveness:
Customer-Centric Focus: Lean manufacturing emphasizes understanding customer needs and preferences. By prioritizing the customer perspective, organizations can align their processes and products to deliver enhanced value. This focus helps in creating a stronger relationship between manufacturers and their clients, ultimately leading to increased loyalty and repeat business.
Cross-Functional Collaboration: Lean manufacturing fosters collaboration across departments, breaking down silos that often hinder communication and efficiency. By encouraging teams to work together, organizations can streamline decision-making processes, reduce delays, and enhance overall productivity. This collaborative spirit is vital for addressing complex challenges and achieving common goals.
Continuous Improvement (Kaizen): The philosophy of Kaizen, or continuous improvement, is central to lean manufacturing. It advocates for incremental changes that collectively lead to significant enhancements over time. Employees at all levels are encouraged to identify inefficiencies and propose solutions, creating a culture of innovation that drives ongoing progress.
Standardization of Processes: Standardizing processes ensures consistency and quality in production. By establishing best practices and documenting them, organizations can reduce variability and errors. This standardization not only enhances quality control but also simplifies training for new employees, leading to quicker onboarding and reduced training costs.
Visual Management: Lean manufacturing employs visual management tools to enhance communication and monitor performance. Techniques such as Kanban boards and visual workflow charts provide real-time visibility into operations, enabling teams to quickly identify issues and make informed decisions. This transparency fosters accountability and drives engagement among employees.
Lean Tools and Techniques
Lean manufacturing employs a variety of tools and techniques designed to facilitate the implementation of its principles:
Value Stream Mapping (VSM): This tool provides a visual representation of the entire production process, highlighting areas of waste and inefficiency. By mapping out the flow of materials and information, organizations can identify bottlenecks and develop targeted strategies for improvement.
5S Methodology: The 5S framework—Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain—focuses on workplace organization and efficiency. By creating a clean and organized environment, companies can reduce waste, enhance safety, and improve overall productivity.
Just-In-Time (JIT) Production: JIT aims to produce and deliver products precisely when they are needed, minimizing inventory levels and associated costs. This approach not only reduces waste but also enhances flexibility, allowing organizations to respond quickly to changes in demand.
Root Cause Analysis (RCA): This problem-solving technique involves identifying the underlying causes of issues rather than merely addressing symptoms. Tools like the "Five Whys" and Fishbone Diagrams help teams conduct thorough analyses, leading to more effective and sustainable solutions.
A3 Problem-Solving: A3 is a structured approach to problem-solving that emphasizes a concise, visual format for documenting issues, analysis, and action plans. This tool encourages clarity and collaboration, making it easier for teams to tackle complex challenges.
Benefits of Lean Manufacturing
The adoption of lean manufacturing principles can yield numerous benefits for organizations across various industries:
Enhanced Operational Efficiency: By streamlining processes and eliminating waste, organizations can significantly improve their operational efficiency. This increased efficiency leads to faster production cycles, reduced lead times, and improved resource utilization.
Improved Product Quality: Lean manufacturing places a strong emphasis on quality control. By focusing on defect prevention and continuous improvement, organizations can deliver higher-quality products, reducing the likelihood of returns and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Cost Reduction: Lean practices lead to substantial cost savings through waste reduction, optimized inventory management, and increased efficiency. By lowering operational costs, organizations can improve their bottom line and invest in further innovations.
Greater Employee Engagement: A culture of continuous improvement fosters greater employee involvement and satisfaction. When employees feel empowered to contribute to problem-solving and process enhancements, they are more likely to be engaged and committed to the organization’s success.
Increased Flexibility: Lean manufacturing equips organizations with the agility to adapt to changing market demands. By employing practices such as JIT and cross-training employees, companies can quickly pivot their operations to meet new challenges.
Sustainable Practices: Lean manufacturing inherently supports sustainability by promoting efficient resource utilization and waste reduction. Organizations adopting lean principles can enhance their environmental performance, reducing their carbon footprint and contributing to corporate social responsibility goals.

Conclusion
Lean manufacturing is not merely a set of practices; it represents a transformative mindset that prioritizes efficiency, quality, and continuous improvement. By adopting lean principles, organizations can navigate the complexities of modern manufacturing, drive operational excellence, and foster a culture of innovation. While challenges may arise during implementation, the long-term benefits of lean manufacturing far outweigh the obstacles. As industries continue to change, embracing lean principles will be essential for organizations striving to thrive in a competitive marketplace and contribute positively to society and the environment.
#LeanManufacturing #WasteReduction #EfficiencyMatters #ContinuousImprovement #Kaizen #ProcessOptimization #ValueStreamMapping #JustInTime#SixSigma #LeanThinking #ManufacturingExcellence #OperationalExcellence #WasteNotWantNot #LeanProduction #SmartManufacturing #ManufacturingInnovation #QualityManagement #SupplyChainEfficiency #ProductivityBoost #LeanTools


Comments